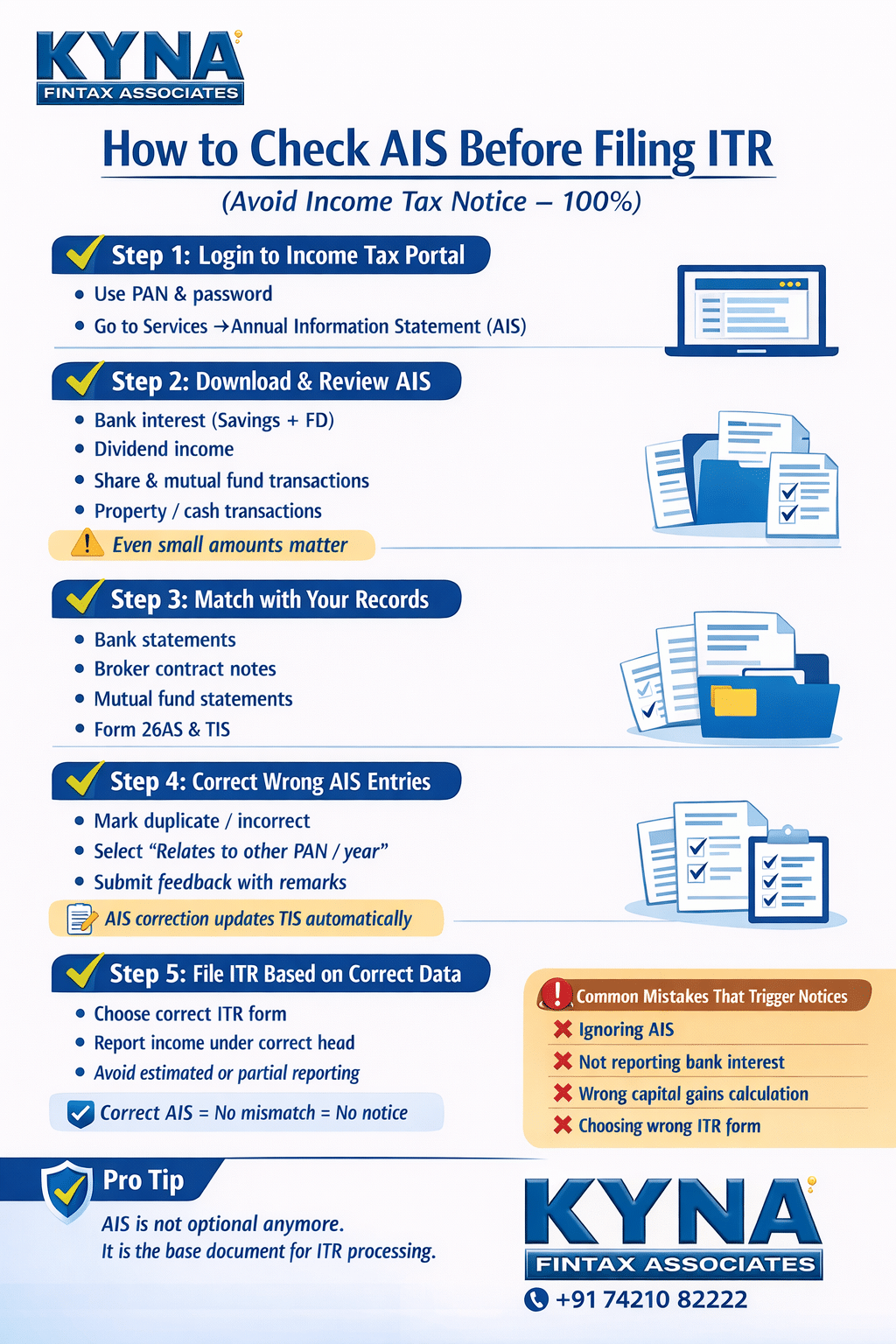
How to Check AIS Before Filing ITR (Avoid Notice 100%)
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) without checking your AIS is one of the biggest and most common mistakes taxpayers make in India today. Many income tax notices — especially mismatch notices — are not issued because tax was intentionally evaded, but simply because the taxpayer ignored or misunderstood the Annual Information Statement (AIS).
The Income Tax Department now has access to highly detailed financial data about every taxpayer. Bank interest, mutual fund investments, dividends, share trading, property transactions, foreign remittances — everything is reported to the department through various reporting entities. AIS is the consolidated reflection of that data.
If your ITR does not match what appears in AIS, the system automatically flags the return. This often results in notices under Section 139(9), 143(1), or even scrutiny notices later.
This blog explains what AIS is, why it is critical, how to check it properly, how to respond to incorrect entries, and how to file your ITR safely to avoid notices almost 100%.
What Is AIS (Annual Information Statement)?
AIS stands for Annual Information Statement. It is a comprehensive statement available on the Income Tax Portal that shows all financial transactions reported against your PAN during a financial year.
AIS is much more detailed than Form 26AS. While Form 26AS mainly focuses on tax deducted (TDS), tax collected (TCS), and advance/self-assessment tax, AIS captures almost every high-value financial transaction linked to your PAN.
AIS includes:
- Bank interest
- Dividend income
- Mutual fund purchases and redemptions
- Share trading (STT-based transactions)
- Property transactions
- Cash deposits and withdrawals
- Credit card payments
- Foreign remittances
- GST-related information (in some cases)
- TDS/TCS entries reported by deductors
The Income Tax Department uses AIS as a primary reference document while processing returns.
Why Checking AIS Before Filing ITR Is Mandatory Now
Earlier, mismatches could sometimes go unnoticed. That is no longer the case.
Today, ITR processing is almost entirely automated. The system cross-verifies your return with:
- AIS
- TIS (Taxpayer Information Summary)
- Form 26AS
- Previous year filings
- Information received from banks, mutual funds, stock exchanges, and other reporting entities
If your ITR does not include income reflected in AIS, the system assumes under-reporting unless you have given a valid explanation.
Common consequences include:
- Defective return notice
- Adjustment under Section 143(1)
- Demand notice
- Loss of refund
- Scrutiny selection
Simply put, ignoring AIS is inviting a notice.
Difference Between AIS and TIS (Important to Understand)
Many taxpayers confuse AIS with TIS.
AIS is the detailed transaction-level data.
TIS is a summarised version of AIS, which the system actually uses while processing your return.
Key points:
- AIS may show duplicate or incorrect entries
- TIS reflects values after system-level aggregation
- Corrections in AIS usually impact TIS automatically
You must review both, but AIS is where corrections are submitted.
How to Check AIS on the Income Tax Portal (Step-by-Step)
Checking AIS is free, easy, and takes less than 5 minutes.
Step 1: Login to Income Tax Portal
Go to the official income tax e-filing portal and log in using your PAN and password.
Step 2: Go to AIS Section
After login:
- Click on “Services”
- Select “Annual Information Statement (AIS)”
You will be redirected to the AIS dashboard.
Step 3: Select Financial Year
Choose the relevant financial year for which you are filing the ITR.
Step 4: Download AIS
You can:
- View AIS online
- Download AIS as PDF
- Download AIS as JSON (useful for professionals)
Always download and keep a copy for records.
What Transactions You Must Check Carefully in AIS
Do not just glance at AIS. You must check each section carefully.
Bank Interest (Savings + FD)
- Interest is often reported by banks even if amount is small
- Many taxpayers ignore interest below ₹10,000 — this is wrong
- Interest must be reported even if no TDS was deducted
Dividend Income
- Dividend from mutual funds and shares is fully taxable
- Even small dividend amounts appear in AIS
- Match with broker statements and mutual fund statements
Share Trading (Equity & Derivatives)
- Sale of equity shares is reported based on STT data
- AIS may show gross sale value, not profit
- Capital gains must be calculated separately and reported correctly
Mutual Fund Transactions
- Redemptions appear in AIS
- Switches between schemes may also appear
- Capital gains need correct classification (short-term or long-term)
Property Transactions
- Purchase or sale of immovable property is reported
- Stamp duty value may be reflected
- Incorrect PAN mapping can sometimes occur
Cash Deposits & Withdrawals
- High cash transactions get reported
- Even genuine business or personal deposits can trigger mismatch if unexplained
Common AIS Errors You Must Watch For
AIS is powerful, but not always correct. Common errors include:
- Duplicate entries
- Transactions belonging to another person wrongly tagged to your PAN
- Gross amounts shown instead of taxable income
- Transactions already exempt but still reported
- Timing mismatch (income of another year)
Never assume AIS is 100% accurate. It is your responsibility to verify and correct it.
How to Submit Feedback or Correction in AIS
AIS allows taxpayers to submit feedback on each transaction.
Types of Feedback Options
You can mark a transaction as:
- Information is correct
- Information is not fully correct
- Information relates to other PAN/year
- Information is duplicate
- Information is denied
You can also enter remarks and revised values where applicable.
Important Points While Giving Feedback
- Provide correct classification
- Do not blindly deny genuine income
- Keep supporting documents ready
- Feedback does not delete income — it updates the system’s understanding
Once feedback is submitted, AIS updates and TIS generally reflects the corrected value.
How AIS Impacts Different ITR Forms
AIS affects all ITR forms — ITR-1, ITR-2, ITR-3, etc.
Examples:
- If AIS shows capital gains, ITR-1 may not be allowed
- If dividend income is present, Schedule OS must be filled
- If share trading appears, capital gains schedules become mandatory
Choosing the wrong ITR form despite AIS data is another major reason for defective returns.
Why Notices Come Even When Tax Is Already Paid
Many taxpayers receive notices despite paying full tax. This usually happens because:
- Income is not shown under correct head
- Schedule mismatch
- Incorrect reporting year
- Income shown net instead of gross
- AIS data ignored
The system does not assume intention. It only checks data mismatch.
Best Practices to Avoid Notice 100%
While no one can guarantee zero notices, following these practices reduces risk drastically:
- Always check AIS before starting ITR filing
- Match AIS with bank, broker, and MF statements
- Report income even if exempt (where disclosure is required)
- Give feedback for incorrect AIS entries
- Use correct schedules and heads of income
- Do not suppress income assuming “small amount doesn’t matter”
- Keep documentation ready for future reference
Should You File ITR Even If AIS Shows No Income?
Yes. Filing ITR is advisable even if AIS shows nil or minimal income, especially if:
- You have carried forward losses
- You want refunds
- You need financial records
- You expect future scrutiny
AIS is only a data source — filing responsibility remains with the taxpayer.
AIS has changed the way income tax returns are filed in India. The days of estimated or casual filing are over. Today, data-driven filing is the only safe way.
Checking AIS before filing your ITR is no longer optional. It is essential.
If you treat AIS as your pre-filing checklist, you significantly reduce the risk of notices, adjustments, and unnecessary stress.
A few minutes spent reviewing AIS can save months of follow-ups later.
Need Professional Help?
If you are unsure how to interpret AIS data, handle mismatches, calculate capital gains, or respond to income tax notices, professional assistance can save time and penalties.
Kyna FinTax Associates
WZ-1390/Z2, 3rd Floor, Nangal Raya Extension,
South West Delhi – 110046
📞 Call / WhatsApp: +91 74210 82222
📧 Email: services@kynafintax.com
🌐 Website: https://kynafintax.com
We assist taxpayers with:
- AIS & TIS reconciliation
- Error-free ITR filing
- Capital gains computation
- Income tax notice handling
- Tax planning and compliance